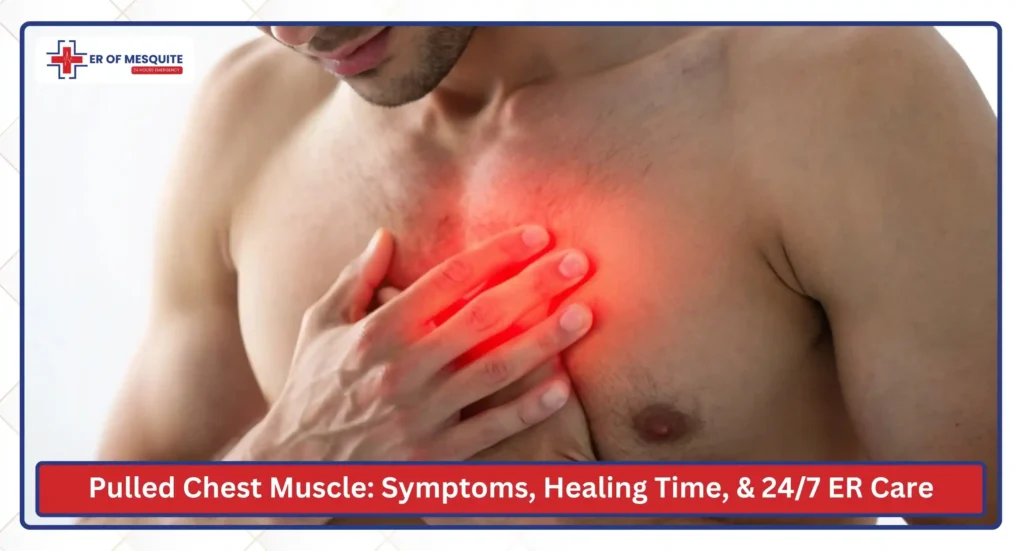
Chest pain appears suddenly, feels sharp, or worsens with movement. While people often assume chest pain is heart-related, a significant amount of non-cardiac chest pain actually comes from chest muscle strain.
A pulled chest muscle can mimic the symptoms of more serious conditions, causing discomfort, tightness, and difficulty moving. Many patients experience chest wall pain, inflammation, or soreness that worsens with deep breathing, twisting, or lifting.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and healing process of a muscle strain in the chest is key to knowing when you can manage symptoms at home and when it’s time to visit the ER of Mesquite for 24/7 chest pain evaluation.
This Pulled Chest Muscle Guide explains the key symptoms, causes, and treatments of chest muscle strain and helps you know when chest pain needs urgent care at the ER of Mesquite.
Understanding Chest Muscle Strains
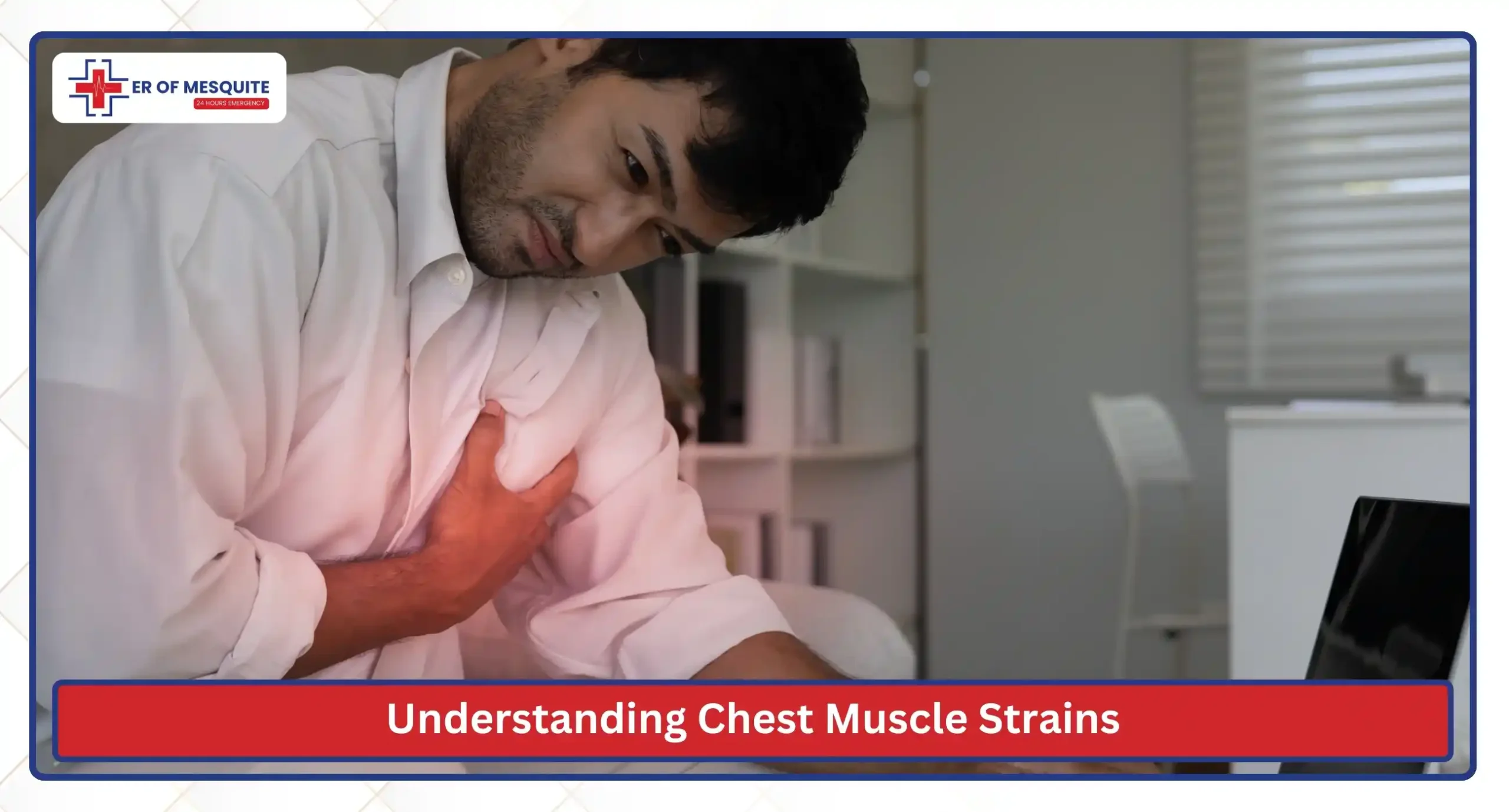
The chest is supported by several major muscles, including the pectorals and the intercostal muscles located between the ribs. These muscles help you breathe, lift, push, and twist.
A muscle strain is a pulled muscle, and when it occurs in the chest, it may lead to:
- Sudden sharp pain
- Pulling or tearing sensations
- Tightness when stretching or lifting
- Pain that feels worse during physical movement
At the ER of Mesquite, our 24/7 emergency service team provides fast, advanced evaluation to determine whether your chest pain is a pulled muscle or a more serious condition requiring immediate attention.
Common Causes of Pulled Chest Muscles
In this Pulled Chest Muscle Guide, it’s important to understand that chest muscle strains often develop from everyday movements. A sudden twist, overstretch, or heavy lift can easily overload the pectoral or intercostal muscles. These small movements can cause inflammation in the chest and difficulty with deep breathing or upper-body motion.
| Reason | How it causes pulled muscle |
| Heavy Lifting / Intense Exercise | Overloads the pectoral or intercostal muscles, causing strain or tearing. |
| Sudden Twisting Movements | Stretches the chest wall muscles beyond normal range, leading to injury. |
| Overstretching During Activity | Creates micro-tears in chest muscles during sports or daily motions. |
| Forceful Coughing / Sneezing | Puts repeated stress on intercostal muscles, causing irritation. |
| Direct Trauma or Impact | Causes immediate bruising or muscle fiber damage. |
Understanding these common triggers helps you protect your chest wall and recognize strain early.
For severe pain, difficulty breathing, or worsening symptoms, the ER of Mesquite’s 24/7 emergency chest pain treatment provides fast, accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Can You Pull a Muscle in Your Chest?
Yes, it’s possible to pull a muscle in your chest. The chest is supported by major muscles like the pectorals and intercostal muscles, which work together to support breathing, arm movement, and upper body strength.
Symptoms of a pulled chest muscle often include chest wall pain, tenderness, swelling, sharp or aching discomfort, and pain that worsens with movement or deep breathing. While most mild strains improve with rest, ice/heat therapy, and over-the-counter pain relief, severe pain or difficulty breathing requires urgent evaluation at the ER of Mesquite to rule out more serious conditions.
Pulled Chest Muscle: How Long to Heal?
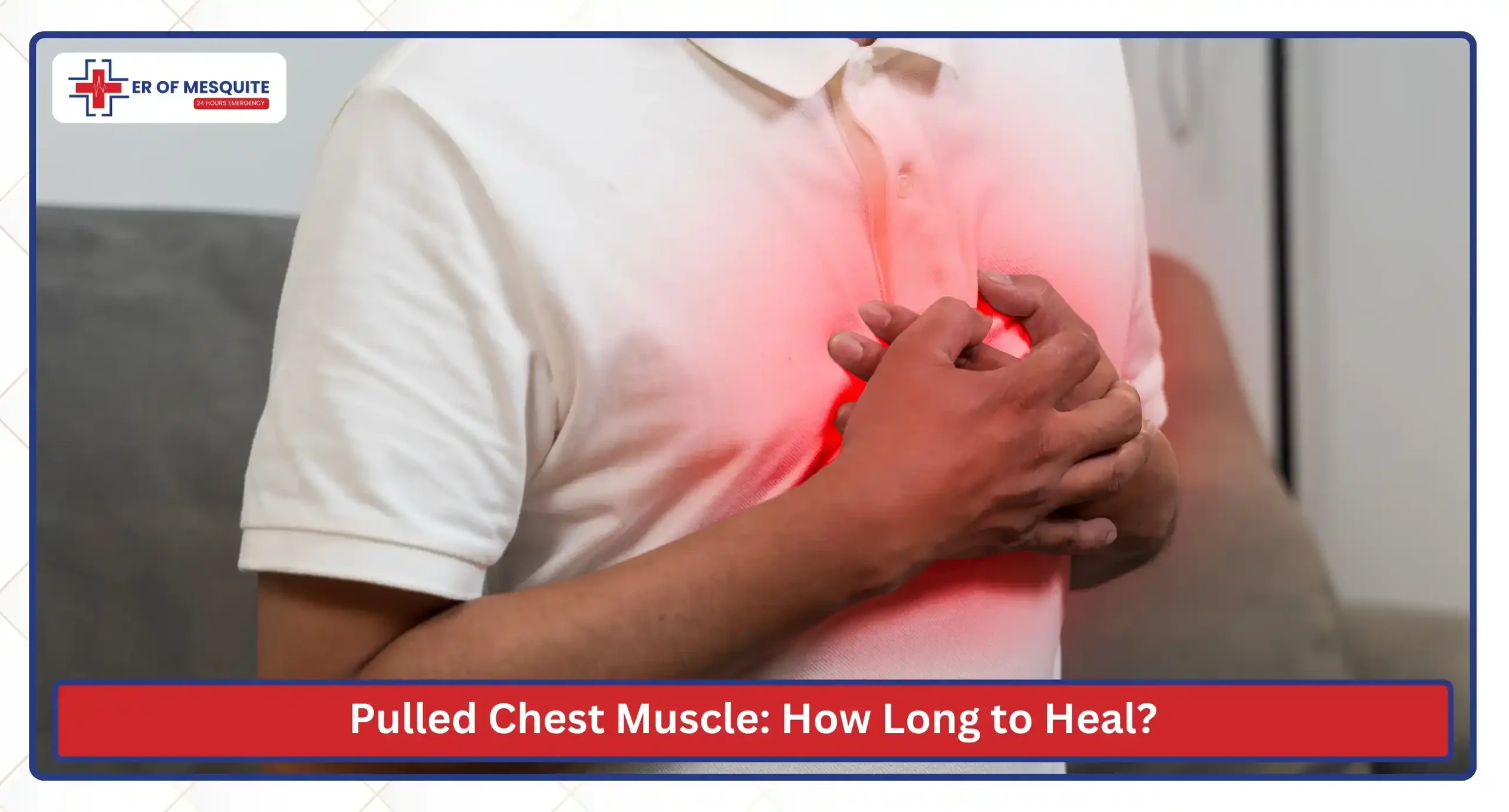
Healing time for a pulled chest muscle depends on how much the chest wall or intercostal muscles were strained. Most people experience chest muscle pain while stretching or deep breathing. Controlling inflammation in the chest and avoiding overuse helps speed up recovery.
The table below illustrates the healing timeline for a pulled chest muscle.
| Severity | Healing Time | Symptoms |
| Mild Strain | 2–3 weeks | Light chest muscle pain, mild tightness |
| Moderate Strain | 3–6 weeks | Noticeable muscle strain in the chest, swelling, and limited motion |
| Severe Strain | 6+ weeks | Sharp pain, weakness, persistent chest wall pain |
Is Chest Pain Often a Pulled Muscle?
No, not all chest pain is heart-related. In many cases, discomfort in the chest can be traced to a pulled chest muscle or chest muscle strain rather than the heart or lungs. Activities like heavy lifting, sudden twisting, or overstretching during exercise can overstress the pectoral or intercostal muscles, leading to chest wall pain, tenderness, and inflammation in the chest.
Seek urgent 24/7 evaluation at the ER of Mesquite
Visit our About Us page to see why patients trust the ER of Mesquite
When to Go to the ER for a Pulled Chest Muscle
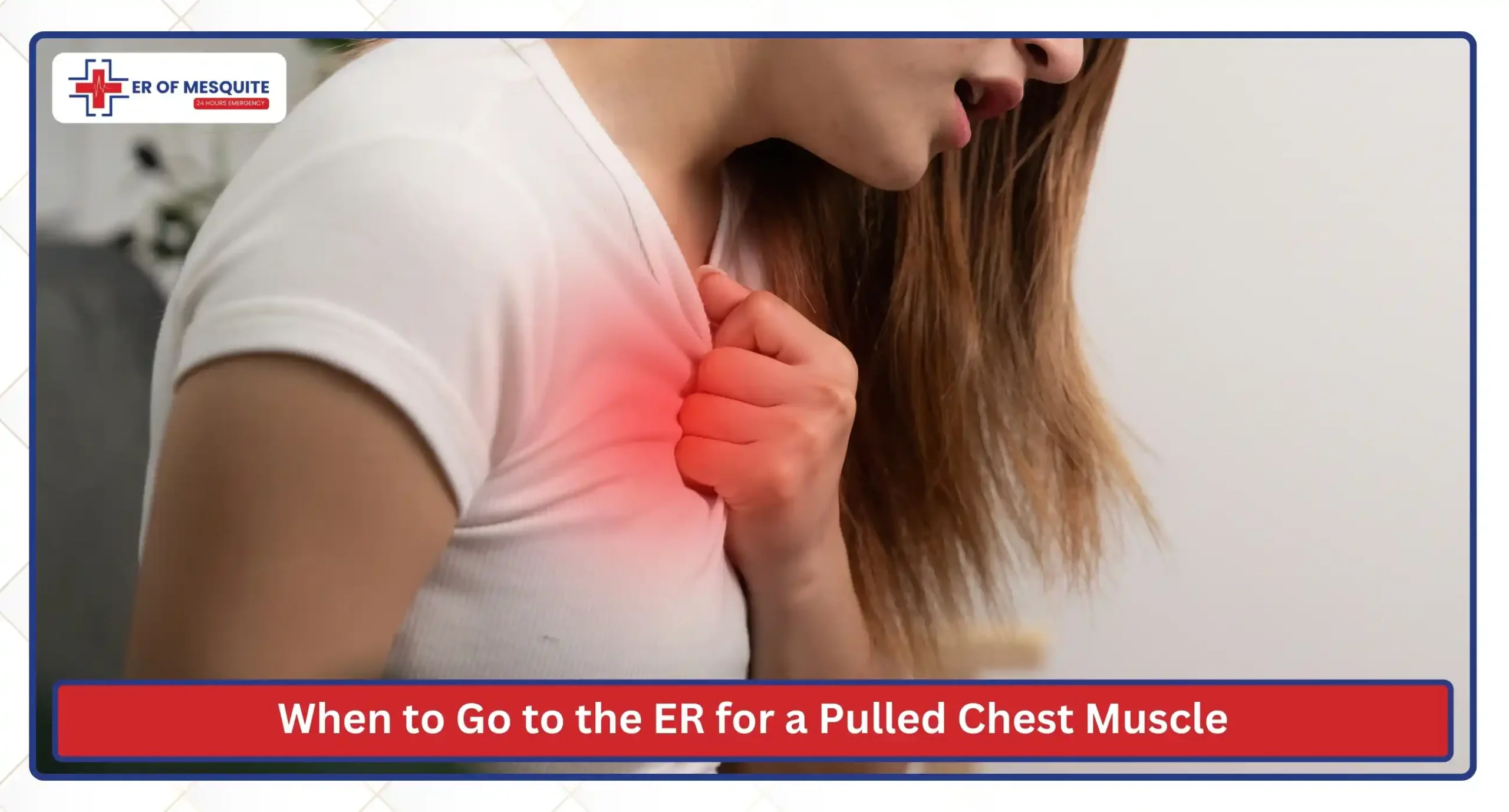
While many cases of chest muscle strain can improve with rest and home care, certain symptoms require urgent evaluation at the ER of Mesquite. You should seek emergency care if you experience:
- Severe or worsening chest pain that doesn’t improve with rest
- Pain radiating to the shoulder, arm, back, or jaw
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing deeply
- Swelling, redness, or bruising around the chest wall
- Sharp pain following trauma from a fall, sports injury, or heavy lifting
- Persistent discomfort that lasts more than a few days despite home treatment
Your Path to Safe, Fast Recovery Starts Here
A pulled chest muscle may seem minor, but chest pain should never be ignored. Early evaluation helps rule out serious medical issues, ensures proper treatment, and speeds up recovery. Understanding symptoms, knowing what triggers chest muscle strain, and recognizing when to seek emergency care can prevent further injury and give you peace of mind.
At the ER of Mesquite, we offer 24/7 access to advanced imaging, rapid diagnosis, and expert care for chest wall pain, muscle strains, and chest injuries. Whether you’re experiencing inflammation, soreness, or sudden sharp pain, our team is here to guide your recovery every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can you pull a muscle in your chest?
Yes, sudden twisting, heavy lifting, or coughing can strain chest muscles.
What are common pulled chest muscle symptoms?
Localized pain, tenderness, swelling, and discomfort during movement or deep breathing.
How long does a chest muscle strain take to heal?
Typically, 2–6 weeks, depending on severity.
Is chest pain always a pulled muscle?
No. Although chest pain is often a pulled muscle, it can also indicate heart or lung issues. Seek emergency care for severe symptoms.
How do you relieve a pulled chest muscle?
Rest, ice/heat therapy, gentle stretching, and OTC pain relief.