The human rib cage is more than a bone and plays a crucial role in protecting the internal organs of the body. It further supports breathing, movement, and posture. An important element of the rib cage is the costal cartilage, also known as rib cartilage.
The costal cartilage plays an important role in musculoskeletal alignment, as it connects the ribs to the sternum. Studying about costal cartilage and about its care is essential because if it gets inflamed, it might cause slipping rib syndrome, costal cartilage pain, or rib subluxation that causes serious discomfort.
In this blog, we will help you understand the anatomy of costal cartilage and important information related to its function, care, and what to do when something goes wrong.
What is Costal Cartilage?
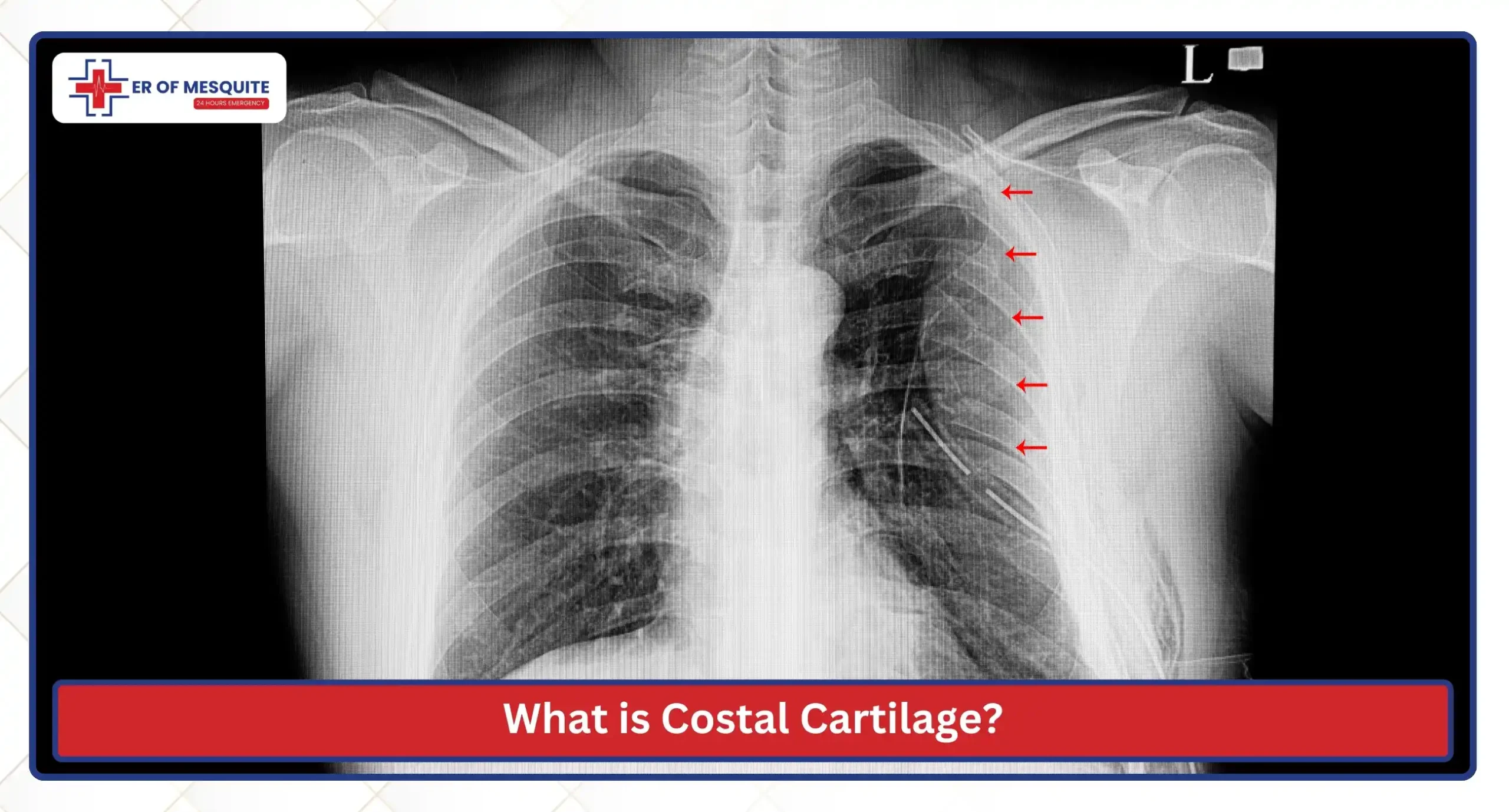
Costal cartilage bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward; they are responsible for the flexibility and support of the ribcage. With the help of costal cartilages, the ribcage protects the internal organs and attains the elasticity required for breathing and movement.
Below is the structural explanation of costal cartilage:
- True Ribs: covers ribs 1-7 and directly connects to the sternum.
- False Ribs: covers ribs 8-10 and indirectly connects to the sternum.
- Floating Ribs: covers ribs 11-12 and does not connect to any cartilage connections and remains unattached.
Preventing Costal Cartilage Injury
Costal cartilage injuries should be taken seriously, as they mimic cardiac-related issues, such as a heart attack. In such critical cases, it is important to visit an emergency room for reliable urgent services immediately. If you experience a sudden discomfort in your chest, then do not hesitate to visit us at the ER of Mesquite to get a quick diagnosis and the best emergency services.
Costal cartilage pain is intense and extremely painful. It affects your daily activities and causes difficulty in breathing, movement, and maintaining a good body posture.
Below are a few prevention techniques for costal cartilage injury:
- Avoid chances of rib strain through maintaining proper posture.
- Do strength exercises for
- Do not overstress the upper body.
- Immediately treat a minor pain.
Types of Costal Cartilage Pain
Costal cartilage plays a vital role in the flexibility and mobility of the chest; a minor pain or inflammation can affect its function. It might result in serious complications that require immediate medical attention. Understanding the most common costal cartilage pain is essential so that you can opt for immediate clinical evaluation.
Slipping Rib Syndrome
It is caused by a rib out of place or a slightly slipped rib, resulting in popping pain. It occurs when the rib is displaced due to torn or weakened cartilage. Most likely, it occurs when the cartilages of ribs 8-10 become unstable.
Rib Subluxation
It occurs when the rib is dislocated at the costal cartilage, resulting in serious strain, injury, and a bad posture. It results in serious pain, especially near the spinous process.
Costochondritis
This happens when the costal cartilages get inflamed, resulting in sharp pain that gets worse while breathing. It usually occurs in the upper ribs, most commonly in ribs 2-5.
Treatment and Diagnosis
Costal cartilage pain, such as slipping rib syndrome, rib subluxation, and rib inflammation, can be treated effectively once they are properly diagnosed. Identifying the cause of pain is the first step to initiating the right treatment.
How to Diagnose Costal Cartilage Pain?
Physical Examination
Once you encounter mild discomfort in your chest, you should instantly visit an emergency room to get it physically evaluated. Observing the physical condition, such as swelling, redness, and tenderness, can help evaluate the severity of the pain.
Imaging
Diagnoses through testing are accurate and more reliable. The root cause of the pain can be diagnosed through digital X-rays. In a few cases, ultrasound and MRI could also be choices, which usually detect pain caused by inflammation.
Treatment Options
The right treatment of costal cartilage is selected based on its cause and severity. Complex issues can be treated through surgeries and medications, whereas mild pain can be resolved through rest and proper diet.
The table below illustrates the common treatment options along with the pain they are best suitable for:
| Treatment Option | Best For | Details |
| Therapies | Rib misalignment and slipping rib syndrome | Different therapies, including stretching, manual therapies and exercises, can be done by physiotherapists. |
| Medications | Mild pain and costal cartilage inflammation | Anti-inflammatory medicines are given to reduce inflammation. |
| Surgery | Serious costal cartilage injuries and severe slipping rib syndrome, | Skeletal traction and removal of damaged costal cartilage. |
| Injections | Persistent inflammation, or Costochondritis | Anti-inflammatory injections in the affected area. |
| Medical Devices | Slow-healing pain and injuries | Devices such as bone stimulator to increase healing through electrical impulses. |
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy of costal cartilage is essential for everyone. It makes you aware of unexpected chest pain and what to do in uncertain conditions. They play a crucial role in breathing, movement, and flexibility of the rib cage.
Whether you’re suffering from slipped rib syndrome, rib inflammation, or rib subluxation, with the proper diagnosis and the right treatment, you can heal quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the early signs of costal cartilage injury?
If you’re experiencing sudden pain in your chest, which gets worse upon breathing, coughing, and moving, then it might be due to costal cartilage injury.
Does stress cause rib pain?
Yes, since stress causes the muscles to get tight or loose, a sudden stress might cause muscle tension resulting in rib pain.
How can costal cartilage pain be treated?
Depending upon the severity of the pain, it can be treated through rest, medications, therapy, or surgery.
Does the ribcage contain the costal cartilage?
The rib cage consists of 24 ribs, whereas the costal cartilage covers ribs 1-12, which generally connect the sternum with the cartilage.